Adaptive Audience (Ongoing)
In VR fitness games, the appearance of non-player characters (NPCs) is very widespread and is used to enhance gameplay experiences. Previous research has revealed that NPC spectators' feedback and reactions could improve players' performance, experience, and exertion. Additionally, research has shown that the size, nature, and volume of the NPC's feedback could vary the impact on player performance.
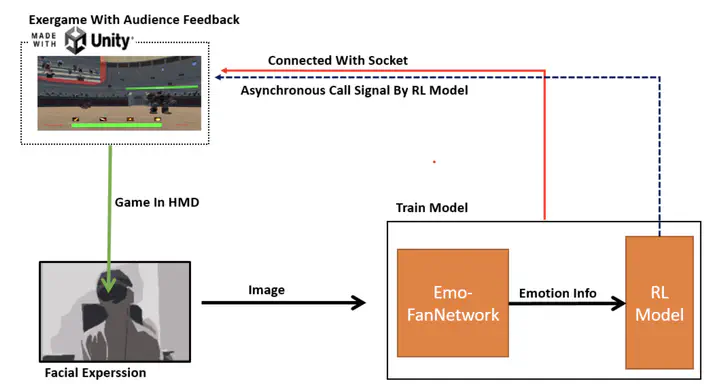
We proposed an adaptive user interface that could enable NPCs to change their feedback dynamically, e.g., different actions, different feedback volumes, and different broadcasting impressions to design an effective and enjoyable user interface in exergames.
Problems: The purpose of having spectator feedback on players’ performance is to give affirmative messages to their actions, showing them that their performance has achieved a certain standard and that they are making progress which should result in positive outcomes. In other words, the ultimate goal of our framework is to prioritize optimizing player experience. Thus, We have 2 problems to solve: -P1: Different players have different preferences. For example, negative feedback might motivate some players, but it could make others feel discouraged. There is no one-for-all criteria to pre-encode a model or algorithm to make the interface adaptive. -P2: It's hard to quantify player experience during the gameplay. Reinforcement Method is more effective when learning from complex, dynamic, and uncertain problems that arise from interactions with the environment. In our current situation, it's difficult to use supervised learning or other models to address this issue. For P1, we use a Reinforcement Learning (RL) approach to learn.
Solutions: P1: Reinforcement Method is more effective when learning from complex, dynamic, and uncertain problems that arise from interactions with the environment. In our current situation, it's difficult to use supervised learning or other models to address this issue. For P1, we use a Reinforcement Learning (RL) approach to learn.
P2: We use Emo-Fan VR. Emo-Fan is a network commonly used to measure a person's psychological state through facial expressions. We use Emo-Fan VR, a version fine-tuned with facial data from a person wearing an HMD, to capture real-time player facial expressions as input for the RL algorithm. In Emo-Fan VR, the output results use two coordinate values, Arousal and Valence, along with a label from "Neutral", "Happiness", "Sadness", and "Surprise". These two psychological dimensional measures are non-discrete and very suitable for use in real-time applications.
More details will be released after publication